avia.wikisort.org - Aerodrome
Reno–Tahoe International Airport (IATA: RNO, ICAO: KRNO, FAA LID: RNO) is a public and military airport three miles (4.8 km) southeast of downtown Reno, in Washoe County, Nevada, United States.[1][3] It is the state's second busiest commercial airport after Harry Reid International Airport in Las Vegas. The Nevada Air National Guard has the 152nd Airlift Wing southwest of the airport's main terminal. The airport is named after both the City of Reno, Nevada and Lake Tahoe.[4] The airspace of Reno-Tahoe Airport is controlled by the Northern California TRACON and Oakland Air Route Traffic Control Center.[5]
Reno–Tahoe International Airport | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Reno–Tahoe Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Reno, Nevada | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Reno, Nevada | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 4,415 ft / 1,346 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 39°29′57″N 119°46′05″W | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www.renoairport.com | ||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||
 FAA diagram | |||||||||||||||||||
 RNO Location  RNO RNO (the United States) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2021) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
History
Early years
The airport was built in 1929 by Boeing Transport Inc. and named Hubbard Field after Boeing Air Transport VP and air transport pioneer Eddie Hubbard.[6] It was acquired by United Airlines in 1936 and purchased by the City of Reno in 1953. The August 1953 OAG shows 15 scheduled departures each weekday; ten years later there were 28.
Jets (United 727s) arrived in June 1964; runway 16 (now 16R) was extended southward from 7800 to 9000 feet around that time. The airport didn't rate a nonstop to Los Angeles until 1969; a nonstop to Chicago began in 1970.
The first terminal building was completed in time for the 1960 Winter Olympics held in Squaw Valley, California in 1960. The present ticketing lobby and concourses were built in 1979.[7] The airport received its current name in 1994 (which honors both the city and the nearby popular tourist destination Lake Tahoe), when the terminal was named in honor of retired Air Force Reserve Major General and former U.S. Senator Howard Cannon.[8] Prior to that the airport itself was named Cannon International Airport.
Reno–Tahoe International was the hub of Reno Air, a now-defunct airline that had MD-80s and MD-90s to many cities until it was bought by American Airlines and later disposed of, in 2001. Reno Air's first flight was on July 1, 1992, and its last flight was August 30, 1999. On New Year's Eve of 2003, Continental Airlines completed the installation of self check-in in the continental United States at Reno International.[9]
Expansion
In 1996, the baggage claim and ticketing area were updated with technology and decor. In 2008, the airport began a $70 million project that enhanced the baggage screening equipment and remodeled the ticketing area with a modern Tahoe theme; the project was entirely completed in 2010. In March 2013, a $24 million expansion of the airport was completed and focused on a new centralized TSA Security Checkpoint on the ground level, and above it, a shopping and dining promenade called "High Mountain Marketplace". Windows in the dining areas allow views of the mountains and runways. Future projects may include updates to the concourses.[10]
International service
In February 2014, the airport announced that Volaris planned to start operating non-stop service flights to Guadalajara, Mexico sometime in 2015. Since the DOT approved the route, it is Reno's first international non-stop service since 1999. On October 7, 2014, the DOT and the airport announced that Volaris would start a twice weekly flight to Guadalajara, Mexico from Reno on December 16, 2014.[11]
In November 2014, Thomas Cook Airlines announced that it planned to introduce twice weekly, non-stop flights from London–Gatwick to Reno starting in December 2015. It would have been the first transatlantic route from Reno Airport.[12] However, Thomas Cook Airlines canceled these plans in May 2015 stating insufficient border control capacities at the airport to handle their Airbus A330.[13][14] Finally, in September 2019, Thomas Cook went into compulsory liquidation.
Facilities
Overview

Reno/Tahoe International Airport covers 1,450 acres (587 ha) at an elevation of 4,415 feet (1,346 m). In the year ending June 30, 2019 the airport had 104,239 aircraft operations, average 285 per day: 46% airline, 41% general aviation, 11% air taxi, and 2% military. At that time 161 aircraft were based here: 104 single-engine, 19 multi-engine, 23 jet, 9 military, and 6 helicopter.[1][15] The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems categorized it as a primary commercial service airport (more than 10,000 enplanements per year).[16]
It has three concrete runways: 16R/34L is 11,001 by 150 feet (3,353 x 46 m); 16L/34R is 9,000 by 150 feet (2,743 x 46 m); 7/25 is 6,102 by 150 feet (1,860 x 46 m).[1] In fall 2010 the airport opened a new 200-foot (61-meter) ATCT to replace the 70-foot (21-meter) control tower that had been used for more than 50 years. It was designed by the Parsons Design Firm, responsible for the design of many other ATCT towers. The cost of the new tower was about 30 million dollars.
The passenger terminal is named after the late US Senator Howard Cannon.[17] The lobby of the terminal has an exhibit with the bust of Nevada State Senator (and Nevada State Senate Minority Leader) William J. "Bill" Raggio. Raggio is described in the exhibit as being "The Father of the Airport Authority."
Military facilities

The airport is also host to Reno Air National Guard Base, an approximately 60-acre (24 ha) complex which was established on the west side of the airport in 1954 when Air National Guard units relocated from the former Stead Air Force Base in Reno.
The base is home to the 152d Airlift Wing (152 AW), a Nevada Air National Guard unit operationally gained by the Air Mobility Command (AMC) and equipped with C-130H Hercules aircraft.
Terminals

Reno–Tahoe International Airport provides two concourses designated B and C with an overall 23 jet bridge gates.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger

| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Alaska Airlines | Portland (OR), Seattle/Tacoma Seasonal: Los Angeles |
| Allegiant Air | Las Vegas |
| American Airlines | Chicago–O'Hare, Dallas/Fort Worth, Phoenix–Sky Harbor |
| American Eagle | Austin, Los Angeles, Phoenix–Sky Harbor |
| Delta Air Lines | Salt Lake City Seasonal: Minneapolis/St. Paul |
| Delta Connection | Los Angeles, Salt Lake City |
| Frontier Airlines | Las Vegas |
| JetBlue | Los Angeles, New York–JFK |
| JSX | Burbank, Las Vegas, Orange County |
| Southwest Airlines | Burbank, Denver, Las Vegas, Long Beach, Los Angeles, Oakland, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, San Diego, San Jose (CA) Seasonal: Dallas–Love, Orange County |
| Spirit Airlines | Las Vegas |
| Sun Country Airlines | Seasonal: Minneapolis/St. Paul |
| United Airlines | Denver, Houston–Intercontinental Seasonal: Chicago–O'Hare, Newark, San Francisco |
| United Express | Denver, Los Angeles, San Francisco Seasonal: Chicago–O'Hare |
| Volaris | Guadalajara |
| Destination maps |
|---|
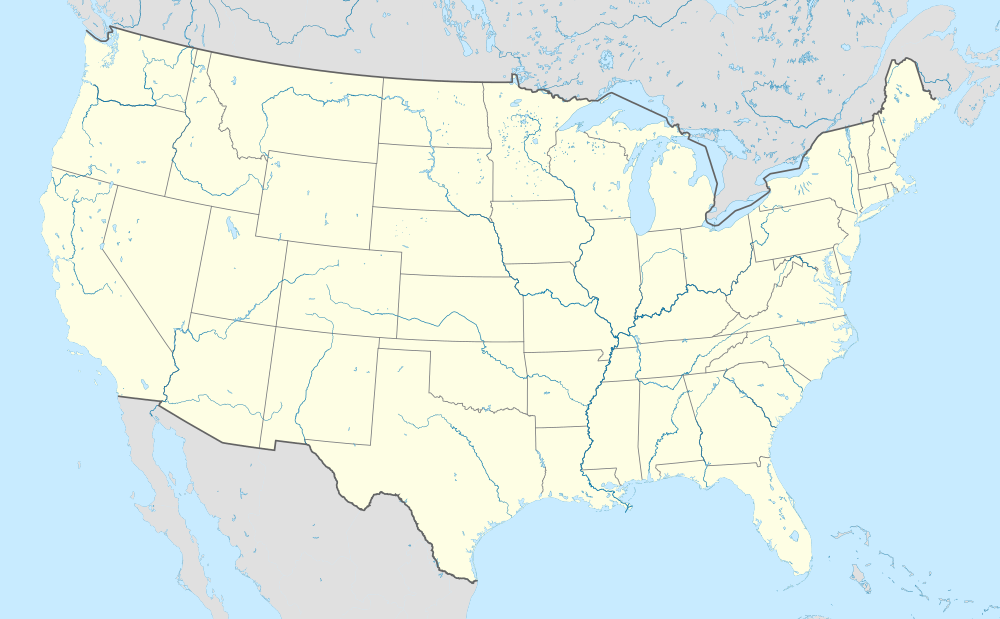 Reno Austin Dallas/Fort Worth Las Vegas Domestic destinations (except California) from Reno–Tahoe International Airport Red = Year-round destination Green = Seasonal destination Blue = Future destination |
California destinations from Reno–Tahoe International Airport Red = Year-round destination Green = Seasonal destination Blue = Future destination |
International destinations from Reno–Tahoe International Airport |
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Ameriflight | Los Angeles |
| DHL Aviation | Denver |
| FedEx Express | Boise, Great Falls, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Memphis, Oakland |
| UPS Airlines | Denver, Des Moines, Louisville, Omaha, Portland (OR), Sacramento–Mather, Seattle–Boeing Seasonal: Kahului, Lubbock, Oakland, Ontario, Philadelphia |
Statistics
Top destinations
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Las Vegas, Nevada | 354,000 | Allegiant, Frontier, Southwest |
| 2 | Denver, Colorado | 254,000 | Frontier, Southwest, United |
| 3 | Los Angeles, California | 229,000 | Alaska, American, Delta, JetBlue, Southwest, United |
| 4 | Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Arizona | 227,000 | American, Southwest |
| 5 | Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas | 153,000 | American |
| 6 | Salt Lake City, Utah | 126,000 | Delta |
| 7 | Seattle/Tacoma, Washington | 121,000 | Alaska |
| 8 | San Francisco, California | 84,000 | United |
| 9 | San Diego, California | 75,000 | Southwest |
| 10 | Long Beach, California | 65,000 | Southwest |
Airline market share
| Rank | Airline | Passengers | Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Southwest Airlines | 1,593,000 | 40.26% |
| 2 | SkyWest Airlines | 663,000 | 16.75% |
| 3 | American Airlines | 584,000 | 14.76% |
| 4 | United Airlines | 264,000 | 6.66% |
| 5 | Delta Air Lines | 216,000 | 5.46% |
| 6 | Other Airlines | 637,000 | 16.10% |
Annual traffic
| Year | Passengers | Change | Year | Passengers | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 5,000,663 | – | 2016 | 3,650,830 | ||
| 2007 | 5,044,087 | 2017 | 4,015,305 | |||
| 2008 | 4,434,638 | 2018 | 4,210,095 | |||
| 2009 | 3,755,935 | 2019 | 4,450,673 | |||
| 2010 | 3,822,485 | 2020 | 2,006,420 | |||
| 2011 | 3,754,155 | 2021 | 3,623,458 | |||
| 2012 | 3,479,122 | |||||
| 2013 | 3,431,986 | |||||
| 2014 | 3,298,915 | |||||
| 2015 | 3,432,657 |
Ground transportation
Car rental
The airport provides convenient access to nine different rental car agencies with rental car pick up available right outside the terminal building. All nine rental car counters are located in the baggage claim. After completing the rental agreement inside, vehicles may be collected from the parking structure located just outside the baggage claim.
Taxis and limousines
The passenger waiting area for taxis and limousines is located outside of the D Doors located north of the baggage claim.
Bus
Public transportation to/from the airport is available via RTC Ride:
- Route No. 12 takes passengers either to Downtown 4th Street Station or Meadowood Mall and stops at Terminal Way & Villanova Street, which is a short walk from the north baggage claim via the marked pedestrian walkway.
- Route No. 19 takes passengers to Downtown 4th Street Station and stops outside the baggage claim. This route operates only on weekdays.
Shuttles
Complimentary hotel shuttles stop along the curb, outside the D Doors located north of the baggage claim, to pick up passengers.
Accidents and incidents
- At 10:15 pm on November 24, 1971, a Northwest Orient Airlines Boeing 727 landed at the airport with the aft airstair still deployed after the aircraft had been hijacked by an unidentified man who is only known as D.B. Cooper. The aircraft had been hijacked by Cooper between Portland, Oregon and Seattle, Washington earlier that day. After landing in Seattle, the passengers were released. Cooper and the crew of the 727 were allowed to depart from Seattle to Mexico City with a fuel stop in Reno. The crew reported that the aft airstair had been deployed while over southern Washington. Upon landing in Reno, the aircraft was surrounded by law enforcement. An armed search quickly confirmed that Cooper was gone. The identity of the hijacker and his whereabouts remain a mystery to this day.
- In the early morning hours of January 21, 1985, Galaxy Airlines Flight 203, a Lockheed L-188 Electra, took off from the airport for Minneapolis, Minnesota and crashed 1.5 miles (2.4 km) southwest of the airport while the pilots were attempting an emergency landing after experiencing an unexpected vibration from under the wing. An investigation attributed the crash to pilot error for failing to maintain proper control over the aircraft while investigating the cause of the vibration. The vibration was later found to be caused by an open air start service door which the ground crew failed to secure before departure. All but one of the 71 passengers and crew on board were killed.
- Also in 1985, Roger Stockham, who would later be arrested for attempting to blow up a mosque in Michigan, was arrested at the airport for planting a pipe bomb and carrying an unregistered weapon.[20]
- On April 13, 2011, a Piper Cheyenne air ambulance flight landed uneventfully at Reno–Tahoe International Airport without a clearance, after the single overnight air traffic controller fell asleep. Federal Aviation Regulations state that if a control tower is not in operation (a condition satisfied by the fact that the controller was asleep), it is considered an "uncontrolled airport" with flight and ground movement becoming the responsibility of the pilot. The incident was minor in nature and safety was never compromised; however, it led to the resignation of Air Traffic Organization chief executive Hank Krakowski.[21] The Federal Aviation Administration announced that 27 airports, including RNO, would subsequently be staffed with two air traffic controllers during graveyard shifts.[22]
Sound levels
Sound levels have been analyzed for over two decades at this airport, with one of the first studies being a comprehensive production of aircraft sound level contour maps.[23] Later analysis was conducted to analyze sound levels at Kate Smith School and provide retrofitting to reduce sound levels through a Federal Aviation Administration grant.[24]
See also
- Reno Stead Airport (RTS), location of the Reno Air Races
References
- FAA Airport Form 5010 for RNO PDF. Federal Aviation Administration. effective August 11, 2022.
- "Statistics". Reno-Tahoe Airport Authority. January 2019. Retrieved April 23, 2019.
- "Cannon International Airport". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- "Reno-Tahoe International Airport Profile | CAPA".
- "AirNav: KRNO - Reno/Tahoe International Airport".
- "William Boeing and Eddie Hubbard make first U.S. delivery of international airmail on March 3, 1919". www.historylink.org.
- "2007–08 budget of the Reno–Tahoe Airport Authority (RTAA)" (PDF). nsla.nevadaculture.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 31, 2014.
- "Airport Fact Sheet" (PDF)., Reno/Tahoe International Airport
- "Continental Airlines Self-Check-In Kiosk Network Expanded to All Domestic U.S. Airports". Continental Airlines. PR Newswire. January 8, 2004. Retrieved March 22, 2017.
- Hidalgo, Jason (April 6, 2022). "'Vastly undersized' Reno airport to expand, upgrade aging infrastructure". Reno Gazette Journal. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- "10-07-2014 – New International Service to Guadalajara Pending Customs Approval". Reno-Tahoe International Airport. October 7, 2014.
- "Thomas Cook Airlines to Launch London Gatwick – Reno Service starting December 2015". airlineroute.net.
- "Nonstop Reno-London flights scrapped". Reno Gazette Journal. Retrieved March 25, 2018.
- "05-07-2015 - London Flight on Thomas Cook is Cancelled". www.renoairport.com. May 8, 2015.
- "RNO airport data at skyvector.com". skyvector.com. Retrieved August 30, 2022.
- "2011–2015 NPIAS Report, Appendix A" (PDF, 2.03 MB). National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems. Federal Aviation Administration. October 4, 2010.
- "Reno/Tahoe International Airport Information - HotelsByCity.net". hotelsbycity.net. Archived from the original on February 12, 2009. Retrieved December 27, 2008.
- "Reno–Tahoe, NV: Reno–Tahoe International (RNO)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- "RITA | BTS | Transtats". Transtats.bts.gov. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- "Terror charges filed in plot to blow up Islamic Center".
- Sonner, Scott (April 14, 2011). "FAA official resigns after sleeping controllers". Associated Press. Washington, D.C. Retrieved April 14, 2011.
- Hidalgo, Jason (April 13, 2011). "FAA two-controller-at-night policy in Reno changed shortly after it was put in place". Reno Gazette-Journal. Reno, Nevada. Retrieved April 14, 2011.
- Vegelatos, Reno Cannon International Airport Contour Maps, prepared for the Reno Cannon International Airport (1985)
- C.Michael Hogan and Ballard George, Aircraft Sound Insulation Study for the Kate Smith School, Sparks, Earth Metrics, prepared for the FAA, January 8, 1988
External links
- Official website

- Reno Air
- Reno Air Fleet Galleries
- "Diagram of Reno/Tahoe International (RNO)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. (21.1 KB) from Nevada DOT
- FAA Airport Diagram for Reno/Tahoe International Airport (PDF), effective November 3, 2022
- FAA Terminal Procedures for RNO, effective November 3, 2022
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KRNO
- ASN accident history for RNO
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KRNO
- FAA current RNO delay information
На других языках
[de] Flughafen Reno-Tahoe
Der Reno-Tahoe International Airport ist ein Flughafen in Reno im US-Bundesstaat Nevada. Er dient auch zur Anbindung des Ski- und Feriengebiets am Lake Tahoe. Außerdem wird er als Reno Air National Guard Base von der Nevada Air National Guard militärisch genutzt.- [en] Reno–Tahoe International Airport
[es] Aeropuerto Internacional de Reno-Tahoe
El Aeropuerto Internacional de Reno-Tahoe (en inglés: Reno–Tahoe International Airport) (IATA: RNO, OACI: KRNO, FAA LID: RNO) es un aeropuerto comercial localizado 5 km al sureste del centro de Reno (Nevada, Estados Unidos). Da servicio al área metropolitana de Reno–Sparks, al oeste de Nevada y a partes del este de California. Es el aeropuerto comercial más cercano al destino de vacaciones y esquí del Lago Tahoe.[fr] Aéroport international de Reno-Tahoe
L'aéroport international de Reno-Tahoe (en anglais : Reno-Tahoe International Airport), également simplement connu en tant qu'aéroport de Reno (code IATA : RNO • code OACI : KRNO), est un aéroport américain situé à Reno, au Nevada. Se trouvant à six kilomètres au sud-est du centre-ville, il s'agit du deuxième aéroport commercial le plus fréquenté de l'État après l'aéroport international McCarran de Las Vegas, avec 4 450 673 passagers qui en font usage en 2019[1].[it] Aeroporto Internazionale di Reno-Tahoe
L'Aeroporto Internazionale di Reno-Tahoe è un aeroporto situato a 6 km a sud est dal centro di Reno Nevada, negli Stati Uniti d'America.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии