avia.wikisort.org - Helicopter
The Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane was an early French experimental quadcopter rotary-wing aircraft developed by Bréguet Aviation.
| Gyroplane No.I and No.II | |
|---|---|
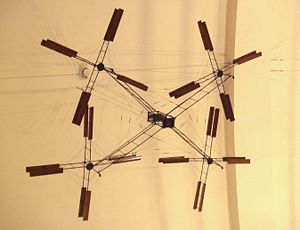 | |
| Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane No.1, 1907. | |
| Role | Rotary-wing test vehicle |
| Manufacturer | Bréguet |
| Designer | Louis Bréguet |
| First flight | 29 September 1907 |
| Number built | 2 |
Design and development
The Gyroplane No.I was one of the earliest attempts to create a practical rotary-wing aircraft. It was designed by the Bréguet brothers with help from Professor Charles Richet. The aircraft had an uncovered open steel framework with a seat for the pilot and a powerplant at the centre. Radiating from the central structure were four wire-braced tubular steel arms, each bearing a superimposed pair of four-bladed rotors. To eliminate the torque effect, two rotor sets were driven clockwise and two counter-clockwise.
Operational service
On 29 September 1907, the Gyroplane No.I was flown for the first time, albeit to an elevation of only 0.6 metres (2.0 ft).[1] It was not a free flight, as four men were used to steady the structure. It was neither controllable nor steerable, but it was the first time that a rotary-wing device had lifted itself and a pilot into the air.[1] It later flew up to 1.52 m (4.99 ft) above the ground. The design was improved and the Gyroplane No.II appeared the following year. No.II had two two-blade rotors of 7.85 m (25.75 ft) diameter and also had fixed wings. Powered by a 41 kW (55 hp) Renault engine, it was reported to have flown successfully more than once in 1908. No.II was damaged in a heavy landing and was rebuilt as the No.IIbis. It flew at least once in April 1909 before being destroyed when the company's works were badly damaged in a severe storm.
Specifications (No.I)
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Height: 3.7 m (12 ft 2 in)
- Empty weight: 500 kg (1,102 lb)
- Gross weight: 578 kg (1,274 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Antoinette water-cooled piston engine, 34 kW (46 hp)
- Main rotor diameter: 4 × 8 m (26 ft 3 in)
- Main rotor area: 402.2 m2 (4,329 sq ft) biplane rotors
Performance
- Endurance: 1 minute
- Service ceiling: 0.6 m (2.0 ft)
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
References
Notes
- Young 1982, p. 28.
Bibliography
- Young, Warren R. The Helicopters. "The Epic of Flight". Chicago: Time-Life Books, 1982. ISBN 0-8094-3350-8.
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing.
- Lacaze, Henri (2016). Les avions Louis Breguet Paris [The Aircraft of Louis Breguet, Paris] (in French). Vol. 2: le règne du monoplan. Le Vigen, France. ISBN 978-2-914017-89-3.
На других языках
- [en] Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane
[fr] Gyroplane Breguet-Richet
Le Gyroplane Breguet-Richet est un aéronef quadrirotor expérimental à voilure tournante, ancêtre de l'hélicoptère avec des ailes flexibles, dont trois prototypes ont été construits en 1907 et 1908. il a été conçu par Louis Charles Breguet avec l'aide de son frère cadet Jacques, polytechnicien, et avec le soutien financier de son parrain, le professeur Charles Richet, savant physiologiste mais aussi un des pionniers de l'aviation en France, ayant conçu un aéroplane dès 1896[1],[2].Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии