avia.wikisort.org - Aeroplane
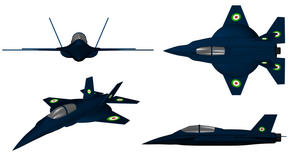
The HESA Shafaq or Shafagh (Persian: هواپیمای شفق, "Twilight" or "Aurora") is an Iranian subsonic stealth aircraft project being developed by the Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Company (HESA).[1]
| Shafaq | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Trainer / Attack aircraft |
| National origin | Iran |
| Manufacturer | Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Company (HESA) |
| Designer | Aviation University Complex |
| First flight | 2017 (forecast, but not achieved) |
| Status | Prototype |
| Primary user | Iran |
| Number built | One prototype |
| Developed from | M-ATF |
Development
According to reports, the Shafaq will be a subsonic aircraft, but this might be changed. Additionally, Iranian Officials have reported that the Shafaq will have a skin of radar-absorbing material.[citation needed]
This two-seat advanced training and attack aircraft appears to be based[2] on the Russian-Iranian "Project Integral" and are fitted with Russian ejection seats. Reportedly, there are plans to produce three versions—one two-seat trainer/light strike version and two one-seat fighter-bomber versions.[1]
The Shafaq is designed by the Aviation University Complex (AUC), part of the Malek-Ashtar University of Technology (MUT). At the start of the program, Iran received help from Russia[2] and the aircraft was known as Integral. Russia later backed away from this project for several reasons[citation needed] and Iran carried on the project by itself renaming it Shafaq. The Shafaq is designed as a sub-sonic aircraft,[2] and made of radar-absorbing material. It has a large leading edge root extension (LERX) and a root aft of the wing which gives it an unusual circular sub-section.[1]
A 1/7 scale model of the Shafaq has already completed testing in the AUC's wind tunnel and pictures have already been revealed which show that a full-scale model has already been built.[2] The Shafaq will be built in different configurations including a two-seater trainer, a two-seater light Attack and a one-seater light attack variants. Roll-out of the first prototype was scheduled for 2008.[citation needed] The Shafaq's advanced cockpit features color MFDs and a Russian-made K-36D ejection seat.
According to AIO (Aerospace Industries Organisation), the aircraft was expected to be flight tested during 2017, and featuring twin, outwardly canted vertical fins. This type of a tail design has become a favoured aerodynamic feature of Iranian designers that dates back to the development of the reverse-engineered Iranian version of the Northrop F-5, the HESA Saeqeh.[3]
Specifications
Data from Trend[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1 or 2
- Length: 10.84 m (35 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 10.45 m (34 ft 3 in)
- Height: 4.26 m (14 ft 0 in)
- Empty weight: 4,361 kg (9,614 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 6,900 kg (15,212 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Klimov RD-33 turbofan engine, 50 kN (11,000 lbf) thrust
Performance
- Service ceiling: 16,780 m (55,050 ft)
- Rate of climb: 110 m/s (22,000 ft/min)
Armament
- Missiles: Sattar, Shahbaz or Fatter missiles
See also
- Equipment of the Iranian Army
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- IAIO Qaher-313
- Hongdu L-15
- Yakovlev Yak-130
Related lists
References
- "Shafaq". globalsecurity.
- Larkins Dsouza (22 September 2007). "Shafaq- Iranian Stealth Plane". defenceaviation.
- "Iranian Shafaq jet trainer nears prototype testing | IHS Jane's 360". www.janes.com. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- "Iran unveiled new indigenous fighter jet". Trend. 2 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 February 2013. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
External links
- GlobalSecurity.org: Shafaq (Before Dawn)
- aeronautics.ru: aka "Vityaz-2000": a Russian based JSF[dead link]
На других языках
[de] HESA Shafaq
Die HESA Shafaq, auch Shafagh genannt (persisch شفق, „Dämmerung“ oder „Aurora“) ist ein iranisches Unterschall-Tarnkappenflugzeug.[1]- [en] HESA Shafaq
[it] HESA Shafaq
L'HESA Shafaq o Shafagh o Shakhab (in persiano شفق, prima dell'alba) è un progetto di velivolo militare concepito per le forze aeree iraniane. Se completato, rappresenterebbe un grosso passo avanti per l'industria aeronautica iraniana, dopo le realizzazioni dell'addestratore Owj Tazarve e dell'HESA Saeqeh / HESA Azarakhsh, versioni del Northrop F-5 ottenute con un'operazione di ingegneria inversaДругой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
