avia.wikisort.org - Weapon
During the Second World War, the Luftwaffe developed a series of unguided rocket-propelled armor-piercing bombs. The three main types were the PC 500 Rs, PC 1000 Rs, and PC 1800 Rs. PC from Panzersprengbombe Cylindrisch ("armor piercing cylindrical bomb") the number from the approximate weight of the bomb in kilograms, and Rs meaning rocket propelled. These bombs were intended to be used against armored ships or similar targets. The purpose of the rocket propulsion was to increase the terminal velocity of the bomb and aid penetration.[1]
| German Rocket Propelled Bombs | |
|---|---|
| Type | Unguided rocket-powered armor-piercing bomb |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Luftwaffe |
| Wars | World War II |
| Production history | |
| Variants | PC 500 RS PC 1000 RS PC 1800 RS PC 1000 Rs EX |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 490 kg (1,080 lb) 987 kg (2,176 lb) 2,057 kg (4,535 lb) |
| Length | 7 ft 2+3⁄4 in (2.203 m) PC 1000 Rs |
| Width | 1 ft 3+1⁄2 in (0.394 m) |
| Warhead | TNT |
| Warhead weight | 119 lb (54 kg) PC 1000 Rs |
Detonation mechanism | Base fuzed |
| Engine | Solid-fuel rocket |
Guidance system | None |
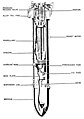
Construction
The three types were similarly constructed with a warhead, spacer, and tail sections:
- Warhead - The warhead was of similar construction to other bombs of the period with thin-walled construction and the filling consisted of alternating layers of high and low-quality TNT. The explosive filling was poured through the base of the warhead. The base of the warhead was threaded and it screwed into the spacer.[1]
- Spacer - The purpose of the spacer was to separate the tail unit from the warhead and it contained a delayed action base fuze for detonating the bomb and a black powder ignition charge. The spacer was also threaded and screwed into the tail unit.[1]
- Tail section - The tail section consists of the following parts: pressure chamber, six venturi tubes, six metal spacers at each end of the pressure chamber, and a spring-loaded pressure release valve. The pressure chamber contained 19 sticks of diglycol dinitrate solid-rocket fuel with the propellant gasses being vented through six venturi tubes that were sealed with pitch until ignited. The pressure chamber also has a spring-loaded pressure release valve in the center for safety. The tail unit also had a total of 12 fins with 4 large fins and 8 small fins for stability.[1]
Operation
The bombs are normally released from a minimum height of 1,200 m (4,000 ft). When the bomb is released an electrical charge is sent to the charging head. This charge is then passed on to both the pyrotechnic fuze and the impact fuze arming the bomb. The pyrotechnic delay is immediately ignited and after 3 or 4 seconds it burns through to the black powder igniter. The solid-rocket propellant burns for three seconds and produces a trail of flame 46 m (150 ft) long. When the bomb hits the target its delayed action base fuze is triggered and the bomb explodes after penetrating the target. [1]
Variants
| Designation | Weight | Diameter | Overall length | Body length | Explosive weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC 500 RS | 490 kg (1,080 lb) | 28 cm (11 in) | 208 cm (6 ft 10 in) | 84 cm (2 ft 9 in) | 14 kg (30 lb 14 oz)[2] |
| PC 1000 RS | 987 kg (2,176 lb) | 36 cm (1 ft 2 in) | 224 cm (7 ft 4 in) | 112 cm (3 ft 8 in) | 54 kg (119 lb 1 oz)[3] |
| PC 1800 RS | 2,057 kg (4,535 lb) | 53 cm (1 ft 9 in) | 269 cm (8 ft 10 in) | 169 cm (5 ft 7 in) | 360 kg (794 lb)[4] |
Gallery
- PC 500 RS
- PC 1000 RS
- PC 1800 RS
See also
- Disney bomb - A 2-ton British unguided rocket-propelled armor-piercing bomb.
References
- "Rocket-Propelled Bomb PC 1000 Rs". Catalog Of Enemy Ordnance Material. Office of the Chief of Ordnance. 1 August 1945. p. 316.
- "PC 500 RS". Luftwaffe Resource Center. Retrieved 2019-01-30.
citing Army Technical manual TM 9-1985-2/Air Force Technical Order TO 39B-1A-9 GERMAN EXPLOSIVE ORDNANCE (Bombs, Fuzes, Rockets, Land Mines, Grenades & Igniters)
- "Luftwaffe Resource Center - Drop Ordnance - A Warbirds Resource Group Site". www.warbirdsresourcegroup.org. Retrieved 2019-01-30.
- "Luftwaffe Resource Center - Drop Ordnance - A Warbirds Resource Group Site". www.warbirdsresourcegroup.org. Retrieved 2019-01-30.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии