avia.wikisort.org - Aeroplane
The Convair R3Y Tradewind was an American 1950s turboprop-powered flying boat designed and built by Convair.
| R3Y Tradewind | |
|---|---|
 | |
| An R3Y-1 Tradewind low over San Francisco Bay near NAS Alameda | |
| Role | transport flying boat |
| Manufacturer | Convair |
| First flight | 22 February 1954 (R3Y-1) |
| Introduction | 1956 (R3Y-1) |
| Retired | 1958 |
| Primary user | United States Navy |
| Number built | 11 (R3Y) & 2 (P5Y) |
Design and development

Convair received a request from the United States Navy in 1945 for the design of a large flying boat using new technology developed during World War II, especially the laminar flow wing and still-developing turboprop technology. Their response was the Model 117. It was a large high-wing flying boat with Allison T40 engines driving six-bladed contra-rotating propellers. It had a sleek body with a single-step hull and a slender high-lift wing with fixed floats. The Navy ordered two prototypes on 27 May 1946. Designated XP5Y-1, the first aircraft first flew on 18 April 1950 at San Diego. In August the aircraft set a turboprop endurance record of eight hours six minutes. The Navy decided not to proceed with the patrol boat version, instead directing that the design should be developed into a passenger and cargo aircraft.
One of the XP5Y-1 prototypes was lost in a non-fatal accident on 15 July 1953, while design and development continued on the passenger and cargo version of the aircraft. The transport and cargo version was designated the R3Y-1 Tradewind and first flew on 25 February 1954. Major changes were the removal of all armament and of the tailplane dihederal, the addition of a 10 ft (3.05 m) port-side access hatch, and redesigned engine nacelles to accept improved T40-A-10 engines. Cabin soundproofing and air conditioning were added for pressurized accommodation for 103 passengers or 24 tons of cargo. As a medevac aircraft, 92 stretcher cases could be carried.

A total of eleven aircraft were built. The first two prototypes built were in P5Y configuration, armed with 8,000 lb (3,600 kg) of munitions (bombs, mines, depth charges, torpedoes) and five pairs of 20 mm cannon in fore and aft side emplacements and a tail turret. The next five were built as R3Y-1 aircraft, intended for troop transport and inflight refueling tanker service. The final six were built as the R3Y-2 variant with a lifting nose and high cockpit (similar in concept to the C-5 Galaxy's nose and cockpit) for heavier transport and landing-ship duties.
The front-loading R3Y-2 aircraft with a hinged nose and high cockpit were intended to be a Flying LST (landing craft). In practice, it was discovered that it was almost impossible for the pilots to hold the aircraft steady and nose on to the beach while the aircraft was loaded or unloaded.[1] The aircraft were converted into tankers for the inflight refueling role. They had a short service life due to unsolvable reliability problems of their Allison T40 turboprop engines, a fate common to most T40-powered aircraft, such as the Douglas A2D Skyshark attack aircraft.
Operational service

The R3Y set a transcontinental seaplane record of 403 mph (649 km/h) in 1954 by utilizing the speed of high-altitude jetstream winds. This record still stands.
After service trials the aircraft were delivered to a U.S. Navy air transport squadron, VR-2, on 31 March 1956. Problems with the engine/propeller combination led to the ending of Tradewind operations and the unit was disbanded on 16 April 1958.
The six R3Y-2s were converted into four-point in-flight tankers using the probe-and-drogue method. In September 1956 one example was the first aircraft to successfully refuel four others simultaneously in flight in 1956, refueling four Grumman F9F Cougars.
The program was halted after thirteen aircraft were built, the reason being the unreliability of the Allison T-40 turboprops. The crash of one of the two XP5Y-1 aircraft was judged due to catastrophic engine failure; when little progress was being made with the engine problems, the Navy halted the program. Subsequently, three more aircraft were lost through engine failures, and the Navy gave up on the T-40 and aircraft powered by it. All the P5Y and R3Y aircraft were grounded in 1958 and subsequently broken up.
Variants
- XP5Y-1
- Prototype patrol flying boat, two built.
- R3Y-1
- Transport aircraft for the United States Navy with side loading door, 5 built.
- R3Y-2
- Assault transport aircraft for the USN with shorter nose incorporating an upward-opening loading door, later converted to four-point tankers for probe-and-drogue operations, six built.
Operators
![]() United States
United States
- United States
- United States Navy
Specifications (R3Y-1)
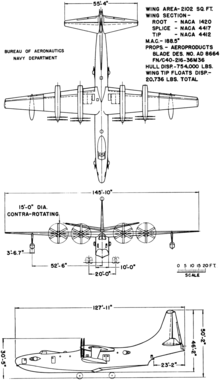
Data from Naval Fighters #34 : Convair XP5Y-1 & R3Y-1/-2 Tradewind[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 7 flight crew + cabin crew / loadmasters
- Capacity: 80 pax / 72 litter patients with 8 medical staff
- R3Y-2: 103 pax / 92 litter patients with 12 medical staff
- Length: 139 ft 8.3 in (42.578 m)
- R3Y-2: 141 ft 1.7 in (43 m)
- Wingspan: 145 ft 9.7 in (44.442 m)
- Width: 12 ft 6 in (3.81 m) maximum hull beam
- Height: 49 ft 0 in (14.94 m) keel to fin tip
- 51 ft 5.2 in (16 m) on beaching gear
- Wing area: 2,100.7 sq ft (195.16 m2)
- Aspect ratio: 10
- Airfoil: root: NACA 1420 ; Mid span NACA 4417 ; tip: NACA 4412 ; average thickness 18%
- Gross weight: 145,500 lb (65,998 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 165,000 lb (74,843 kg)
- Landing weight: 136,739 lb (62,024 kg) with maximum cargo
- Fuel capacity: 66,000 lb (29,937 kg)
- Powerplant: 4 × Allison T40-A-10 turboprop engines, 5,332 shp (3,976 kW) each
- Propellers: 6-bladed Aeroproducts, 15 ft (4.6 m) diameter contra-rotating fully-feathering reversible propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 299 kn (344 mph, 554 km/h) at 21,000 ft (6,401 m) at MTOW
- 308 kn (354 mph; 570 km/h) at 23,000 ft (7,010 m) at normal gross weight
- Cruise speed: 300 kn (350 mph, 560 km/h) average at 29,000–34,200 ft (8,839–10,424 m)
- Stall speed: 98 kn (113 mph, 181 km/h) at MTOW power off
- 89.4 kn (102.9 mph; 165.6 km/h) at 136,739 lb (62,024 kg) power off
- 87.5 kn (100.7 mph; 162.1 km/h) at 136,739 lb (62,024 kg) with approach power
- Range: 2,420 nmi (2,780 mi, 4,480 km)
- Combat range: 1,240 nmi (1,430 mi, 2,300 km)
- Service ceiling: 30,300 ft (9,200 m) at MTOW
- Rate of climb: 1,910 ft/min (9.7 m/s) at MTOW
- Time to altitude: 20,000 ft (6,096 m) in 12 minutes 18 seconds at MTOW
- 30,000 ft (9,144 m) in 43 minutes 12 seconds
- Wing loading: 78.5 lb/sq ft (383 kg/m2) at MTOW
- Power/mass: 0.1293 hp/lb (0.2126 kW/kg) at MTOW
- Take-off time: 50 seconds in calm sea conditions at MTOW
See also
Related lists
- List of United States Navy aircraft designations (pre-1962)
- List of flying boats and floatplanes
References
Notes
- Ginter 1996, p. 94.
- Ginter, Steve (1996). Naval Fighters #34 : Convair XP5Y-1 & R3Y-1/-2 Tradewind (1st ed.). Simi Valley CA: S. Ginter. ISBN 0942612345.
Bibliography
- Door, Robert F. "Beyond the Frontiers: Convair R3Y Tradewind 'The Flying LST'" Wings of Fame, Volume 18, December 1999, Aerospace Publishing, ISSN 1361-2034
- Ginter, Steve. Convair XP5Y-1 & R3Y-1/2 Tradewind. Simi Valley, Calif.: Ginter Books, 1996. ISBN 0-942612-34-5.
- Gunston, Bill. "Turbo Tradewind" Aeroplane Monthly, Volume 20, Issue 01, 1992
External links
- Convair R3Y Tradewind articles and publications
- World's First Turboprop Flying Boat, July 1950, Popular Science article with photos of XP5Y-1
На других языках
[de] Convair R3Y
Die Convair R3Y Tradewind war ein amerikanisches Flugboot mit Turboprop-Antrieb von 1954, das zur Luftbetankung und als Truppentransporter verwendet wurde.- [en] Convair R3Y Tradewind
[fr] Convair R3Y Tradewind
Le Convair R3Y Tradewind (Alizé) est un hydravion américain de transport des années 1950 ayant servi dans les rangs de la United States Navy. Une version de patrouille maritime a également été développée, mais sans suite.[it] Convair R3Y Tradewind
Il Convair R3Y Tradewind era un idrovolante a scafo centrale prodotto dall'azienda aeronautica statunitense Convair negli anni cinquanta.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии