avia.wikisort.org - Aeroplane
The Grumman AF Guardian was the first purpose-built anti-submarine warfare (ASW) carrier-based aircraft to enter service with the United States Navy.[1] It consisted of two airframe variants, one for detection gear, the other for weapons. The Guardian remained in service until August 1955, when it was replaced by the twin-engined Grumman S-2 Tracker. The Guardian was the largest single-engine piston-powered carrier aircraft ever to see service.[2]
| AF Guardian | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Hunter-Killer team of AF-2W (lower) and AF-2S | |
| Role | Anti-submarine aircraft |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Grumman |
| First flight | 19 December 1945 |
| Introduction | October 1950 |
| Retired | 31 August 1955 |
| Status | Replaced by S-2 Tracker |
| Primary user | United States Navy |
| Number built | 389 |
Design and development

The original design concept for the aircraft that would become the Guardian, the XTB2F of 1944, was for a twin-engined aircraft with a 3,600 lb (1,600 kg) warload and a range of 3,700 mi (5,950 km).[3] This was considered to be too large for practical use from an Essex-class aircraft carrier, and was cancelled in 1945, replaced by a modified Grumman F7F Tigercat, the XTSF-1.[4]
However, this too was considered impractical,[5] and another alternative, the internally developed Grumman Model G-70, was selected instead, being given the Navy designation XTB3F-1. This was designed as mixed-power aircraft, with a Pratt & Whitney Double Wasp radial engine in the nose and a Westinghouse 19XB (J30) turbojet in the tail.[4] Originally, the Westinghouse engine was to be the new X24C, which was to emerge as the J34. When it became apparent the X24C delivery schedules would not meet the airframe schedule, the 19XB-2B was substituted. This was found to be unsuitable, and the jet engine was removed without ever having been used in flight.[4] The XTB3F-1S carried a crew of two seated side by side and an armament of two 20 mm cannon and 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) of bombs, torpedoes and/or rockets, and made its first flight on 19 December 1945.[4]
On 24 December 1945, the Navy changed the role of the aircraft from torpedo-bomber to anti-submarine warfare. All the required equipment could not be fitted into a single aircraft, consequently two variants would be produced, one as a "guppy" (hunter) and another as a "scrapper" (killer).[6] The hunter aircraft would not carry any armament,[2] but instead two additional crew members and a ventral radome for AN/APS-20 search radar and electronic countermeasures (ECM) consisting of an AN/APR-98 countermeasures receiver and AN/AP-70 bearing indicator.[7] This aircraft, the XTB3F-1S, first flew in November 1948.[4] The "killer" deleted the cannon of the torpedo bomber, but retained the bomb bay, added a third crewmember, a searchlight, and short-range radar, and (as the XTB3F-2S) first flew in January 1949.[4]
Operational history

Redesignated as AF-2W (TB3F-1S) and AF-2S (TB3F-2S), the Guardian entered fleet service on 27 September 1950 with three aircraft delivered to VS-24,[8] with full service introduction shortly after[9] with VS-25.[10] A total of 193 AF-2S Guardians were built.[9] In 1952, the AF-3S (hunter) was introduced, fitting a magnetic anomaly detector (MAD) for the detection of submerged submarines; 40 of this variant were built.[9] The last Guardian was delivered to the Navy in March 1953,[9] with a total of 389 built.[4]
The Guardian saw service in the maritime patrol role during the Korean War, however it proved unpopular with pilots, being underpowered and heavy on the controls; the aircraft suffered from a severely high accident rate.[4] Shortly after the end of the war, it began to be replaced by the Grumman S2F Tracker,[9] the U.S. Navy first purpose-built ASW airplane to combine the hunter and killer roles in a single airframe.[11] The last AF retired from active service on 31 August 1955,[4] but it remained in service with the US Naval Air Reserve until 1957.[4]
Variants
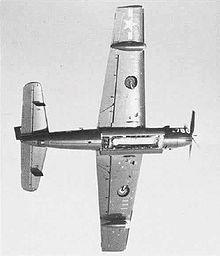
- XTB3F-1
- Prototypes of two-seat torpedo bomber powered by one 2,300 hp R-2800-46 engine and a Westinghouse turbojet; three built.[4]
- XTB3F-1S & -2S
- Two modified XTB3F-1 prototypes with turbojet removed and ventral radome, later redesignated as XAF-1.[4]
- AF-2S
- Production variant with 2,400 hp R-2800-48 engine, 193 built.[9]
- AF-2W
- Hunter variant with search radar in a ventral radome, 153 built.[9]
- AF-3S
- Hunter/Killer variant similar to AF-2S with retractable MAD boom, 40 built.[9]
- Grumman Model G-90
- Proposed combined AF-2S/-2W version, cancelled.
Operators

 United States
United States
- United States Navy
- Aero Union
Surviving aircraft

After disposal by the U.S. Navy five Guardians saw many years service with Aero Union based at Chico, California, in the forest firefighting role, the last being retired in 1978.
- On display
- AF-2S
- 123100 - National Naval Aviation Museum at NAS Pensacola in Pensacola, Florida. It was the seventh AF-2S produced. The aircraft was operated as a firefighter until 1978. It was acquired by the museum in 1980. It is displayed in the colors of its first Navy assignment, though still carries the number "30" on the cowling, which for many years was the aircraft's call-sign as a firefighting aircraft;[12]
- 129233 - Pima Air and Space Museum, Tucson, Arizona. This aircraft is displayed as it appeared while serving as an aerial firefighter with Aero Union in California. During this period the distinctive empennage with twin vertical stabilizers on each horizontal tail were removed to make a more conventional appearance.[13]
- 126731 - Static display at the Commemorative Air Force's facility in Dallas, Texas, as a memorial to VAdm James B. Stockdale, who flew this aircraft early in his Navy career.126731[14][15]
Specifications (AF-2S Guardian)

Data from United States Navy Aircraft since 1911.
General characteristics
- Crew: three[4]
- Length: 43 ft 4 in (13.21 m)
- Wingspan: 60 ft 8 in (18.49 m) (about 25 ft-wings folded (7.62 m)
- Height: 16 ft 2 in (5.08 m)
- Wing area: 560 sq ft (52.03 m2)
- Empty weight: 14,580 lb (6,613 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 22,640 lb (10,270 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-2800-48W "Double Wasp" radial engine, 2,400 hp (1,790 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 253 mph (510 km/h, 276 kn) at full throttle not to exceed 30 minutes at 15,000 ft (4,600 m) with a gross weight 21,000 lbs (9500 kg)
- Range: 1,500 mi (2,415 km, 1,304 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 15,000 ft (4,600 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,850 ft/min (9.4 m/s)
Armament
- Rockets: 6× 5 in (127 mm) unguided High Velocity Aircraft Rockets (HVAR)
- Bombs: 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) of bombs, torpedoes, and depth charges
See also
- List of attack aircraft
- List of military aircraft of the United States
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Bréguet 960 Vultur
- Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf
- Douglas XTB2D Skypirate
- Fairey Gannet
- Fairey Spearfish
- Grumman TBF Avenger
- Grumman S-2 Tracker
- Nakajima B6N
- Short Seamew
References
Notes and Citations
- Kowalski 1991, p. 3.
- Donald and March 2001, p. 46.
- Kowalski 1991, pp. 2–3.
- Goebel, Greg. "Grumman AF Guardian." VectorSite, 2009. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.
- Norton 2008, p. 120.
- Kowalski 1991, p. 16.
- Kowalski 1991, p. 18.
- Kowalski 1991, p. 14.
- Swanborough and Bowers 1990, p. 246.
- Wagner 1982, p. 498.
- Donald and March 2001, p. 50.
- "AF-2S Guardian/Bu. 123100." Warbird Directory: Grumman Page 26 Retrieved: 21 September 2022.
- "AF-2S Guardian/Bu. 129233." Pima Air & Space Museum. Retrieved: 23 December 2021.
- "FAA Registry: N9993Z" FAA.gov Retrieved: 29 July 2021.
- "AF-2S Guardian/Bu. 126731." Warbird Directory: Grumman Page 26 Retrieved: 21 September 2022.
Bibliography
- Donald, David and Daniel J. March. Carrier Aviation Air Power Directory. Norwalk, CT: AIRtime Publishing, 2001. ISBN 1-880588-43-9.
- Goodall, Geoffrey. Warbirds Directory. Victoria, Australia: Victoria Publishing, Fourth Edition 2005.
- Gunston, Bill. Grumman: Sixty Years of Excellence. New York: Orion Books, 1988. ISBN 0-517-56796-2.
- Kowalski, Robert J. Grumman AF Guardian. Naval Fighters Series (#20). Simi Valley, CA: Steve Ginter Publishing, 1991, ISBN 0-942612-20-5.
- Pilot's Manual for Navy Model AF-2S Aircraft, AN 01-85DAB-1. Washington: Secretary of the Air Force and the Bureau of Aeronautics, 4 March 1951; reissued in digital DVD version as Grumman AF-2S Flight Manual, AN 01-85DAB-1, 1951. Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada: Sicuro Publishing Inc., 2011.
- Salerno, Giorgio. Hand-in-Hand: US Navy 'Hunter-Killer' Anti-Sub Teams. Air Enthusiast 111, May/June 2004, pp. 32–37. ISSN 0143-5450
- Swanborough, Gordon and Peter M. Bowers. United States Navy Aircraft since 1911. London: Putnam, Second edition, 1976. ISBN 0-370-10054-9.
- Swanborough, Gordon and Peter M. Bowers. United States Navy Aircraft since 1911. London: Putnam, Third edition, 1990. ISBN 978-0-87021-792-0.
- Thruelsen, Richard. The Grumman Story. New York: Praeger Publishers, Inc., 1976. ISBN 0-275-54260-2.
- Wagner, Ray. American Combat Planes. New York: Doubleday & Company, Third Edition, 1982. ISBN 0-385-13120-8.
External links
- (1951) AN 01-85DAB-1 Pilot's Handbook for Navy Model AF-2S Aircraft[permanent dead link]
- Grumman AF Guardian at Greg Goebel's Air Vectors
- AF2S Guardian at Arizona Wing Commemorative Air Force
На других языках
[de] Grumman AF
Die Grumman AF Guardian war ein U-Boot-Abwehrflugzeug (ASW) der United States Navy. Die Guardian ist bis heute das größte jemals in Serie produzierte einmotorige Kolbenmotorflugzeug.[1]- [en] Grumman AF Guardian
[fr] Grumman AF Guardian
Le Grumman AF Guardian est le premier avion de lutte anti-sous-marine embarqué à bord de porte-avions à être entré en service dans l'aéronavale des États-Unis. Il a été construit à moins de 400 exemplaires et utilisés en service actif de 1950 à 1955. Sa conception imposait l'emploi d'une patrouille mixte avec un AF-2W Guardian de détection et un AF-2S Guardian d'attaque volant ensemble.[it] Grumman AF Guardian
Il Grumman AF Guardian era un monomotore da pattugliamento marittimo ASW imbarcato prodotto dall'azienda statunitense Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation tra i tardi anni quaranta ed i primi anni cinquanta.[ru] Grumman AF Guardian
Грумман AF «Гардиан»[2] (англ. Grumman AF Guardian) — американская палубная противолодочная система, состоявшая из двух однотипных самолётов: AF-2W, который был оснащён радаром APS-20 для обнаружения подводных лодок, и носителя противолодочного оружия AF-2S.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии