avia.wikisort.org - Engine
The Reaction Motors LR99 engine was the first large, throttleable, restartable liquid-propellant rocket engine. Development began in the 1950s by the Reaction Motors Division of Thiokol Chemical Company to power the North American X-15 hypersonic research aircraft. It could deliver up to 57,000 lbf (250 kN) of thrust with a specific impulse of 279 s (2.74 km/s) or 239 s (2.34 km/s) at sea level. Thrust was variable from 50 to 100 percent, and the restart capability allowed it to be shut down and restarted during flight when necessary.
| LR99 | |
|---|---|
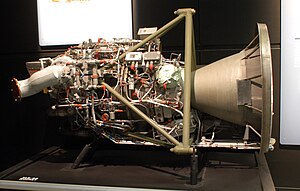 | |
| An XLR-99 rocket engine. | |
| Type | Liquid-propellant rocket engine |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Reaction Motors |
| Major applications | North American X-15 |
Design and development
The engine is propelled by liquid oxygen and anhydrous ammonia, pumped into the engine by turbopumps at a mass flow rate of over 10,000 lb (4,500 kg) per minute.
After one hour of operation, the XLR99 required an overhaul. Operating times nearly twice that were recorded in tests, but declared largely unsafe. The basic X-15 aircraft carried fuel for about 83 seconds of full-powered flight, while the X-15A-2 carried fuel for just over 150 seconds. Therefore, each XLR99 was capable, in theory, of between 20 and 40 flights before an overhaul.
Like many other liquid-fuel rocket engines, the XLR99s used regenerative cooling, in that the thrust chamber and nozzle had tubing surrounding it, through which the propellant and oxidizer passed before being burned. This kept the engine cool, and preheated the fuel. The basic engine has a mass of 910 lb (410 kg).
Operational history
The LR-99 was used exclusively to power the X-15 research aircraft after initial trials that used a pair of Reaction Motors XLR11s.
Applications
Variants
- XLR99-RM-1
- prototype engines for initial testing and flight trials.
- YLR99-RM-1
- Service test engines fitted to X-15s for later flights.[1]
Specifications (YLR-99-RM-1)
Data from Aircraft engines of the World 1964/65[1]
General characteristics
- Type: liquid-fuelled rocket engine
- Length: 82 in (2,083 mm)
- Diameter: 39.3 in (998 mm) at the nozzle
- Dry weight: 910 lb (412.8 kg)
- Fuel: liquid ammonia (LNH3)
- Oxidiser: liquid oxygen (LO2 / LOX)
Components
- Pumps: turbopumps 200 lb/s (90.7 kg/s) driven by High-test peroxide (H2O2) decomposed by a catalyst
Performance
- Thrust: 15,000 lbf (66.72 kN) to 57,000 lbf (253.55 kN)
- Combustion chamber temperature: 4,982 °F (3,023 K; 2,750 °C)
- Combustion chamber pressure: 600 psi (4,137 kPa)
- Specific impulse: 239 seconds
- Propellant consumption:0.0035 lb/lbf/s (0.36 kg/kN/s)
- Burn time:
- Thrust-to-weight ratio: 62:1
See also
References
- Wilkinson, Paul H. (1964). Aircraft engines of the World 1964/65 (20th ed.). London: Sir Isaac Pitman & Sons Ltd. p. 39.
External links
- Reaction Motors XLR99 Rocket – National Museum of the United States Air Force
- XLR-99
На других языках
[de] Reaction Motors XLR99
Der Reaction Motors XLR99 war der erste große, regelbare, wiederstartbare Flüssigtreibstoff-Raketenmotor.- [en] Reaction Motors XLR99
[fr] Reaction Motors XLR99
Le Reaction Motors XLR99 est un moteur-fusée développé par le motoriste américain Reaction Motors pour propulser l'avion-fusée expérimental North American X-15. Il était capable de fournir une poussée de 254 kN avec une impulsion spécifique de 279 secondes dans le vide (239 secondes au sol). La poussée était modulable de 50 à 100 % et il pouvait être redémarré en vol. Le moteur consommait un mélange d'oxygène liquide et d'ammoniac avec une consommation de 4,5 tonnes par minute. Le premier exemplaire du X-15 emportait 83 secondes de carburant pour ses vols tandis que le second pouvait en emporter pour 150 secondes. Comme tous les moteurs-fusées à ergols liquides, la chambre de combustion et la tuyère étaient refroidis par circulation d'ergols. Le moteur avait une masse à sec de 413 kg.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
