avia.wikisort.org - Aeroplane
The PZL M28 Skytruck is a Polish STOL light cargo and passenger plane, produced by PZL Mielec, as a development of licence-built Antonov An-28s. Early licence-built planes were designated PZL An-28. The maritime patrol and reconnaissance variants are named PZL M28B Bryza ("sea breeze").
| PZL M28 Skytruck / Bryza | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | STOL transport and patrol aircraft |
| Manufacturer | PZL Mielec |
| Design group | Antonov/PZL Mielec |
| First flight | 22 July 1984 (PZL An-28) 24 July 1993 (PZL M28 Skytruck) |
| Status | In active service |
| Primary users | Polish Air Force Polish Navy Venezuelan Army United States Air Force |
| Produced | 1984-1993 (PZL An-28) 1993- (PZL M28 Skytruck) |
| Number built | 200+ (including PZL An-28) |
| Developed from | Antonov An-28 |
Development

The Antonov An-28 was the winner of a competition against the Beriev Be-30 for a new light passenger and utility transport for Aeroflot's short haul routes, conceived to replace the highly successful An-2 biplane. The An-28 is derived from the earlier An-14. Commonalities with the An-14 include a high wing layout, twin fins and rudders, but it differs in having a reworked and longer fuselage, with turboprop engines. The original powerplant was the TVD-850, but production versions are powered by the more powerful TVD-10B, with three-blade propellers.
The An-28 made its first flight as the An-14M in September 1969 in the USSR. A subsequent preproduction aircraft first flew in April 1975. Production of the An-28 was then transferred to Poland's PZL Mielec in 1978, although it was not until 22 July 1984 that the first Polish-built production aircraft flew. The An-28's Soviet type certificate was awarded in April 1986.
PZL Mielec has become the sole source for production An-28s. The basic variant, not differing from the Soviet one, was designated PZL An-28 and was powered with PZL-10S (licence-built TVD-10B) engines. They were built mostly for the USSR, until it broke up. The plane was next developed by the PZL Mielec into a westernised version powered by 820 kW (1100shp) Pratt & Whitney PT6A-65B turboprops with five-blade Hartzell propellers, plus some western (BendixKing) avionics (a distinguishing feature are exhaust pipes, sticking out on sides of engine nacelles). Designated the PZL M28 Skytruck, the first flight was on 24 July 1993 and it is in limited production, mostly for export (39 produced by 2006). The type received Polish certification in March 1996, and US FAR Part 23 certificate on 19 March 2004.
Apart from the Skytruck, PZL Mielec developed a family of militarized light transport and maritime reconnaissance planes for the Polish Air Force and Polish Navy in the 1990s, with original PZL-10S engines, named PZL M28B in the Air Force and Bryza in the Navy. From 2000, newly produced M28Bs started to be equipped with five-blade propellers as well.
PZL Mielec was bought by Sikorsky in 2007. Purchased primarily to produce helicopter structures, the company also produces 10 M28s per year.[1] Sikorsky's current owner, Lockheed Martin, has marketed it to the governments of Indonesia, Jordan, Poland, Venezuela, Vietnam, the U.S. and commercial operators. Split equally between commercial and military applications, it competes with the Viking Air Twin Otter, the Let 410 and the Dornier 228.[1]
Design

The M28 is a twin-engined high-wing strutted monoplane with an all-metal airframe, twin vertical fins and a tricycle fixed landing gear. If an engine fails, a spoiler forward of the aileron opens automatically on the opposite wing.[2] This limits the wing drop to 12° in five seconds instead of 30°.[3]
It is capable of Short takeoff & landing (STOL) and hot and high altitude operations.[1] Aerodynamically deployed leading edge slats when approaching stall speed enable a 64 kn (119 km/h) low stall speed and while the certification landing field is 1,640 ft (500 m), PZL has demonstrated landing in 512 ft (156 m).[1] Inlet air ducts inertial separators and inverted configuration of the PT6 and the high wing configuration protect the engines and propellers against foreign object damage for unprepared runways operations.

Multiple configurations are available: a 19-passenger airliner with 2-1 seating and an underbelly luggage pod; a cargo aircraft with a 1,540 lb (700 kg) hand-cranked hoist option; the most common combi; a VIP transport; a medevac for six litters and seven seats; a search-and-rescue version; a 17-seat paratrooper drop version; an 18-passenger utility cabin and an aerial firefighting version is considered.[1] A crew of two can switch between passenger and cargo configurations in 7 min.[1] Its inward opening rear doors allow for cargo drops and utility operations as well as the passenger boarding.[1]
It can take off in 1,800 ft (550 m) at the 16,534 lb (7,500 kg) MTOW.[1] Maximum payload is 5,070 lb (2,300 kg), it can carry 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) over 100 nmi (190 km) or 2,500 lb (1,100 kg) with full fuel over 700 nmi (1,300 km).[1]
Operational history
176 An-28s and M28s in all variants were built in Poland by 2006. Most numerous users are former Soviet civil aviation and the Polish Air Force and Navy (about 25 as of 2006), smaller numbers are used by the Polish civil aviation and in the United States, Nepal, Colombia, Venezuela, Vietnam and Indonesia.
On 4 November 2005, a Vietnamese Airforce M28 crashed in Gia Lam district, Hanoi. All three crewmembers were killed.[4]
On 12 February 2009, The weekly periodical Air Force Times reported that the Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC) would receive 10 PZL M28 Skytrucks in June 2009.[5] These aircraft carry the U.S. Air Force model design series (MDS) designation of C-145A Skytruck. In 2011 one aircraft crash landed in Afghanistan and was damaged beyond repair.[6] 11 of AFSOC's C-145As were retired in 2015. In 2016, three were sent to Kenya, two to Costa Rica, two to Nepal, and two to Estonia.[7]
Variants

Airframe variants
- PZL An-28
- Original variant, built under Antonov licence, with PZL-10S (licensed TV-10B) engines.
- PZL M28 Skytruck
- Development variant with redesigned fuselage and wings, new Pratt & Whitney Canada engines, new (western) avionics, 5-blade rotors, and some other minor changes.
- PZL M28B Bryza
- Militarized variants used by Polish Air Force and Polish Navy, similar to Skytruck, but with PZL-10S engines. Uses partially retracting landing gear to avoid interfering with its radar.[8]
- PZL M28+ Skytruck Plus
- Prototype of new lengthened variant with more internal space, not in production.
- C-145A[9]
- Variant flown by USAF Special Operations Warfare Center. Similar to Skytruck, but with Pratt and Whitney PT6A-65B Turboprops. The USAF has started retiring the aircraft, with the first aircraft, AF Ser. No. 08-0310, delivered to the 309th Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Group at Davis-Monthan AFB, Arizona on 28 May 2015. By June 2015 eleven out of 16 aircraft were stored.[10]
- MC-145B Wily Coyote[11]
- In May 2021, the U.S. Special Operations Command (SOCOM) awarded a contract to Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) to demonstrate the MC-145B as part of the Armed Overwatch program, which is seeking to acquire a new manned light attack aircraft to support U.S. special operations forces in permissive environments. Renderings of the proposed aircraft depict a pair of sensor turrets (one under the nose and the other under the fuselage) as well as a pair of underwing hardpoints on each side (total four) outboard of the wing struts. Internally, eight reloadable Common Launch Tubes (CLT) are provided as well as a ramp-launch capability.
Variants in use by Polish military

- PZL An-28TD
- Basic transport variant. Used mainly for transport and paratroop training (2 built).
- PZL M28B
- Several similar improved transport variants featuring avionics and airframe upgrades: Bryza 1TD (2 built), M28B (3 built), M28B Salon (1 built), M28B TDII, TDIII and TDIV (2 built of each).
- PZL M28B Bryza 1R
- Maritime patrol and reconnaissance variant (equipped with: 360° Search and Surveillance Radar ASR-400, Link-11 datalink). Used mainly for sea border patrolling, search and rescue operations and protection of the national economical sea zone (7 built).
- PZL M28B Bryza 1E skydiving
- Maritime ecological reconnaissance and patrol variant (2 built).
- PZL M28B Bryza 1RM bis
- Maritime patrol and reconnaissance variant with submarine detection capability, of 2004 (equipped with: 360° Search and Surveillance Radar ARS-800-2, ejection of single-use hydro-acoustic sonobuoys, Thermal Imaging System (FLIR), magnetic anomaly detector, Link-11 datalink). Used mainly for sea border patrolling, search and rescue operations and protection of the national economical sea zone (1 built as of 2006).
- PZL M28 05 Skytruck
- Maritime patrol and SAR variant for the Polish Border Guard, of 2006 (equipped with Search and Surveillance Radar ARS-400M and FLIR system) (1 built as of 2006).
Operators
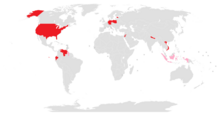
Civil operators
 Germany
Germany
- PD Sicherheit, German defense training contractor, received three aircraft in 2019.[12]
 Guyana
Guyana
- JAGS Aviation Guyana operates one aircraft.
 Indonesia
Indonesia
- Indonesian National Police operates four aircraft.
 United States
United States
- Sierra Nevada Corporation operates two aircraft.
- Arizona Department of Public Safety operates two aircraft.
Military operators

 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Ecuador
Ecuador
- Ecuadorian Army has one in service as of September 2018, purchased to replace crashed IAI Arava.[16][17]
 Estonia
Estonia
- Estonian Air Force received two ex C-145A donated by the US Air Force, first received in March 2019.[18][19]
 Germany
Germany
- Luftwaffe leased two aircraft from private company PD Sicherheit for use in paratrooper training since 2017[12]
 Jordan
Jordan
- Royal Jordanian Air Force
- No.3 Squadron RJAF received three aircraft in 2014 of which one is used for electronic warfare[20]
 Kenya
Kenya
- Kenyan Air Force received the first M28 from the US in February 2021 and second in June 2021. Third one is expected to be delivered in near future[21] Commissioned into service in April 2021.[22]
 Nepal
Nepal
- Nepalese Army Air Service received three (with further two on order)[23]
 Poland
Poland
- Polish Air Force operates 25 aircraft.
- Polish Navy operates 16 aircraft.
- Polish Border Guard operates one aircraft.
 United States
United States
- United States Air Force
- Air Force Special Operations Command
- 318th Special Operations Squadron (2007-2013)
- 6th Special Operations Squadron (2012-)
- Air Force Reserve Command
- 711th Special Operations Squadron (2013-)
- Air Force Special Operations Command
 Venezuela
Venezuela
- Venezuelan Army operates 12 aircraft.
- Venezuelan National Guard operates 13 aircraft.
 Vietnam
Vietnam
Accidents and incidents
- On 28 October 2010, an Indonesian Police-operated M28 crashed in the Nabire region of the Indonesian state of Papua, killing five people.[26]
- On 3 December 2016, a PZL Skytruck belonging to the Indonesian National Police crashed into the ocean in Dabo, Riau Islands while carrying 13 people. All 13 people on board were killed in the accident. Eyewitnesses stated that the aircraft had suffered an in-flight failure and claimed that the engine of the plane was emitting black smoke.[27]
- On 30 May 2017, a PZL Skytruck belonging to the Nepal Army with registration NA-048 crashed at Bajura-based Kolti airport while its pilot was trying to land the aircraft. The cargo airplane was supposed to land on the Simikot airport in Humla district. However, bad weather condition forced the pilot to divert towards Bajura. The pilot of the aircraft died while two others were injured.[28]
Specifications (PZL M28)

Data from Sikorsky[29]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: 19 passengers (17 paratroopers) / 2,300 kg (5,071 lb)
- Length: 13.1 m (43 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 22.06 m (72 ft 5 in)
- Height: 4.9 m (16 ft 1 in) * Cabin Length: 5.26 m (17 ft)
- Cabin Width: 1.73 m (5 ft 8 in)
- Cabin Height: 1.72 m (5 ft 8 in)
- Cabin Volume: 15.65 m2 (168 sq ft)
- Wing area: 39.72 m2 (427.5 sq ft) [30]
- Aspect ratio: 12.25
- Airfoil: TsAGI R-II-14 (14%)[31][32]
- Empty weight: 4,354 kg (9,599 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 7,500 kg (16,535 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 1,766 kg (3,893 lb) / 2,278 l (602 US gal; 501 imp gal)
- Powerplant: 2 × Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-65B turboprop engines, 820 kW (1,100 hp) each
- Propellers: Hartzell HC-B5MP-3D10876ASK
- Propellers: 2.83 m (9 ft 3 in) diameter five-blade fully feathering reversible constant-speed propellers[32]
Performance
- Maximum speed: 355 km/h (221 mph, 192 kn)
- Cruise speed: 244 km/h (152 mph, 132 kn)
- Stall speed: 120 km/h (75 mph, 65 kn)
- Minimum control speed: 153 km/h (95 mph, 83 kn) (VMCA)[32]
- Range: 1,592 km (989 mi, 860 nmi) at 3,281 m (10,764 ft)) with 45 min. reserve
- Ferry range: 3,100 km (1,900 mi, 1,700 nmi) with ferry tanks in the cabin[32]
- Endurance: 6.2 h (3,048 m (10,000 ft), 45 min reserve)
- Service ceiling: 7,620 m (25,000 ft)
- g limits: +3 -1[32]
- Rate of climb: 12.29 m/s (2,419 ft/min)
- Time to altitude: 3,000 m (9,843 ft) in 6 minutes with air bleed off (9 min with air bleed on)[32]</bvre.
- Take-off run: 548 m (1,798 ft)
- Landing run: 499 m (1,637 ft)
- Fuel Consumption: 268 kg/h (591 lb/h)
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter
- Let L-410 Turbolet
- IAI Arava
- Dornier 228
- Harbin Y-12
- CASA C-212
- Shorts Skyvan
- GAF Nomad
- Cessna 408 SkyCourier
References
- John Croft (11 July 2017). "Sikorsky Seeks Sales For Fixed-Wing PZL M28". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- "Flight standardization board report - PZL M28". FAA. 17 May 2006.
- Gerard Frawley. The International Directory of Civil Aircraft.
- vietbao.vn. "Yêu cầu Bộ Quốc phòng điều tra nguyên nhân vụ rơi máy bay M28".
- "AFSOC to get first 10 Skytrucks - Air Force News | News from Afghanistan & Iraq - Air Force Times". www.airforcetimes.com. Archived from the original on 18 July 2012. Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- Ranter, Harro. "ASN Aircraft accident PZL-Mielec C-145A (M28-05) Skytruck 08-0319 Walan Rabat Landing Zone".
- "Kenya seeking Skytruck aircraft from US". defenceWeb. 7 December 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
In July 2015 AFSOC announced it was retiring two-thirds of its C-145A fleet, with 11 aircraft subsequently being disposed of.
- http://www.pzlmielec.pl/oferta/produkty/m28-bryza/wersje-samolotu/ (in Polish)
- "C-145A Combat Coyote". Air Force.
- "United States Withdrew 2/3 of the Polish M28 Skytruck Aircraft From The Active Service". defence24.com.
- Trevithick, Joseph (30 June 2021). "Meet The MC-145B Wily Coyote Armed Special Ops Transport Plane". TheWarZone. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- "Delivery to Germany". m28aircraft.com. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- "Costa Rica offered ex-USAF C-145As". www.keymilitary.com. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- "Kenya Air Force receives first C-145 aircraft". airrecognition.com. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- Defensa.com (22 April 2021). "Los misteriosos C-145 de Costa Rica excedentes de la Fuerza Aérea de Estados Unidos-noticia defensa.com - Noticias Defensa Centro América". Defensa.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- Sanchez, Alejandro (19 April 2018). "Ecuadorian Army to receive M28 airlifter". IHS Jane's 360. Washington, DC. Archived from the original on 21 April 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- Pablo Segovia Renteria, Antonio (31 August 2018). "Ecuadorian Army receives M28 Skytruck". IHS Jane's 360. Santiago. Archived from the original on 31 August 2018. Retrieved 2 September 2018.
- Jennings, Gareth (4 February 2019). "Estonia to receive donated C-145As this year". Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 4 February 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2019.
- Jennings, Gareth (19 March 2019). "Estonia receives first of two donated C-145As". Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 19 March 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- "World Air Forces 2020". FlightGlobal.
- "Kenya Air Force receives first C-145 aircraft".
- "Kenya Air Force commissioned newly acquired C-145 Skytruck aircraft".
- Jennings, Gareth (4 March 2019). "Nepal to receive M28 tactical airlifters from United States". Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 4 March 2019. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 November 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Trung Quốc lo ngại sát thủ Su-30MK2V, M28, 1241.8 của Việt Nam". PhuNuToDay (in Vietnamese). 6 July 2012. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- "Death toll rises to 5 from Indonesian police plane crash". Xinhua News Agency. 28 October 2010. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- "Potongan Jasad Korban Ditemukan dan Langsung Dibawa ke RS Bhayangkara Batam". Tribun News. Retrieved 2 January 2017.
- "Pilot killed, 2 injured as NA cargo airplane crashes in Bajura". myrepublica.com. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- "General informations : performance". PZL Mielec M28. Lockheed Martin / Sikorsky. 2017.
- "Type certificate data sheet n. A.058" (PDF). EASA. 3 November 2015.
- Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- Jackson, Paul, MRAeS, ed. (2005). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 2004-05. London: Jane's Publishing Group. pp. 363–364. ISBN 978-0-7106-2614-1.
External links
- PZL M28 aircraft dedicated website
- List of all PZL M28 aircraft used by Polish Air Force
- An-28/M28/M28B production list
На других языках
[de] PZL M28
Die PZL M28 Skytruck ist ein Kurzstrecken-Transportflugzeug des polnischen Herstellers PZL Mielec. Sie entstand aus der sowjetischen Antonow An-28. Die von zwei Turboprops angetriebene M28 zeichnet sich durch STOL-Eigenschaften (Startstrecke: 325 m) aus und kann von behelfsmäßigen Flugfeldern aus operieren. Erhältlich ist sie in einer Passagierversion mit 19 Sitzplätzen, wie auch in einer Frachtversion (3085 kg Nutzlast), als Sanitätsflugzeug und als Militärtransporter. Eine leicht veränderte Version der M28 wird unter der Bezeichnung M28B Bryza (Seewind, Brise) angeboten. Die Maschine hat keine Druckkabine.- [en] PZL M28 Skytruck
[fr] PZL M28 Skytruck
Le PZL M28 Skytruck est un avion de transport léger polonais, produit par PZL Mielec, en tant que développement de l'Antonov An-28 construit sous licence. Les premiers avions construits sous licence ont été désignés PZL An-28. Les variantes de patrouille maritime et de reconnaissance sont appelées PZL M28B Bryza («brise marine»).[it] PZL Mielec M28
Il PZL Mielec M28 (conosciuto anche con il nome Skytruck) è un aereo da trasporto leggero progettato e prodotto dall'azienda aeronautica polacca Polskie Zakłady Lotnicze, sviluppato dall'Antonov An-28. Possiede capacità STOL ed è impiegato sia in ambito militare che civile.[ru] PZL M28
PZL M28 — модифицированный польский двухмоторный самолёт укороченного взлёта и посадки.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии